Recent Works
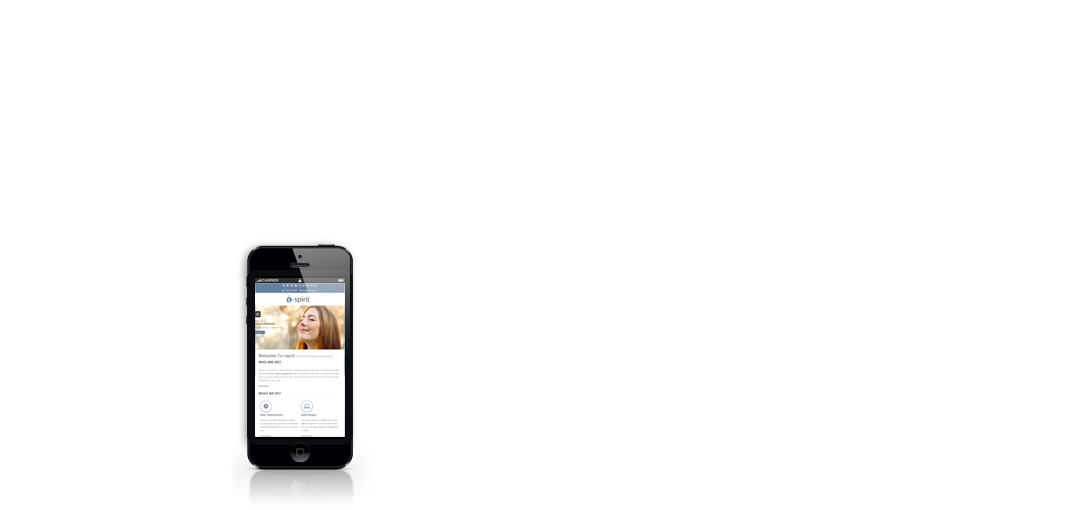
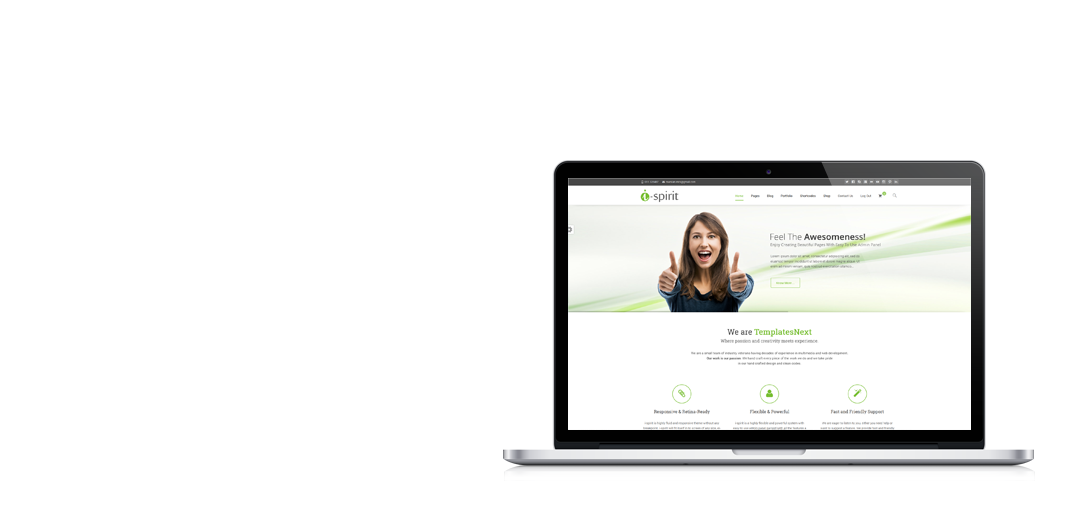
i-spirit, crafted with love and passion
i-spirit features
- Easy to use admin panel options.
- Responsive and retina ready
- Portfolio, Testimonial, Team, etc.
- Unlimited color options.
- 65+ shortcodes and counting
- Translation ready



Contact Us
We would love to hear from you
TemplatesNext, where creativity meets technology.

Recent Posts
Qubely: A Complete Plugin Solution for Any Website
Qubely: A Complete Plugin Solution for Any Website Qubely is no longer a new name to those who are already familiar with WordPress and Gutenberg. It is a revolutionary plugin by ...
Header Customization for Free WordPress Themes
Most of the WordPress themes specially the free ones comes with a fixed header layout or options with little customization. If you are a WordPress user looking for a flexible theme ...
How to Re-Energize a Business Using A Creative Digital Agency WordPress Theme
All organisms need food to stay alive and grow. Your company looks like a living organism. It also needs vitamins to get energy and withstand competition on the market. A powerful ...
10 Best WordPress Gutenberg Themes 2019 You Have Likely Missed Out
When on the hunt for modern and Gutenberg themes, search no more. Become one of the fewest who tried the benefits of Gutenberg editor. Whether you’re using Gutenberg editor or not, ...


